Organization
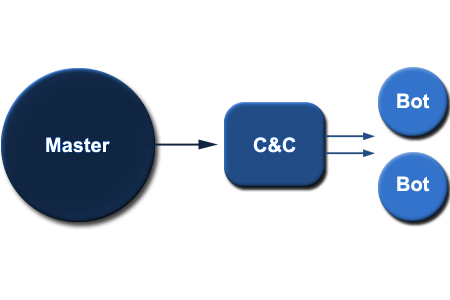
A botnet’s originator (known as a “bot herder” or “bot master”) can control the group remotely, usually through IRC, and often for criminal purposes. Though rare, more experienced botnet operators program command protocols from scratch. These protocols include a server program, a client program for operation, and the program that embeds the client on the victim’s machine. This server is known as the command-and-control (C&C) server. The bots communicate over a network, using a unique encryption scheme for stealth and protection against detection or intrusion into the botnet.
A bot typically runs hidden and uses a covert channel to communicate with its C&C server. Generally, the perpetrator has compromised multiple systems using various tools (exploits, buffer overflows, as well as others; see also RPC). Newer bots can automatically scan their environment and propagate themselves using vulnerabilities and weak passwords. Generally, the more vulnerabilities a bot can scan and propagate through, the more valuable it becomes to a botnet controller community. The process of stealing computing resources as a result of a system being joined to a “botnet” is sometimes referred to as “scrumping.”
A few important aspects about to note how botnets have countered measures against them are:
-
Botnet servers are typically redundant, linked for greater redundancy so as to reduce the threat of a takedown. Actual botnet communities usually consist of one or several controllers that rarely have highly developed command hierarchies; they rely on individual peer-to-peer relationships.
[2] -
Botnet architecture evolved over time, and not all botnets exhibit the same topology for command and control. Advanced topology is more resilient to shutdown, enumeration or discovery. However, some topologies limit the marketability of the botnet to third parties.
[3]Typical botnet topologies are star, multi-server, hierarchical and random. -
Some botnets are scaling back in size to minimize detection. As of 2006, the average size of a network was estimated at 20,000 computers.
[4]
Reference Many-to-Many Botnet Relationships[1]
Reference What is a Botnet trojan?[2]
Reference Botnet Communication Topologies[3]
Reference Hackers Strengthen Malicious Botnets by Shrinking Them[4]